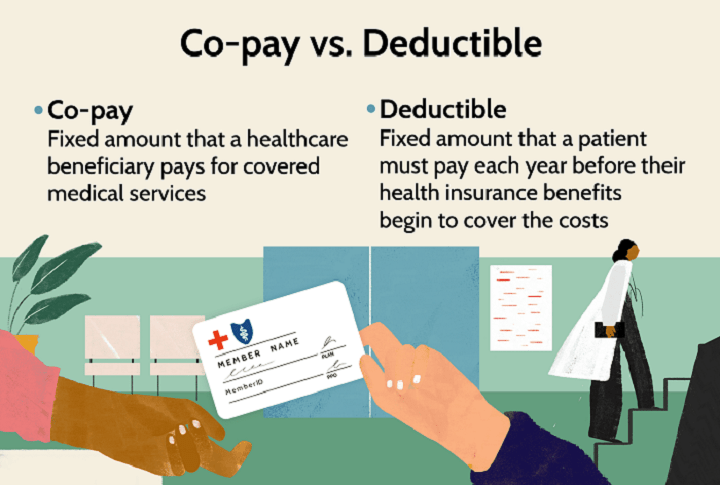
In the complex world of health insurance, understanding key terms and concepts is crucial. One such term that often confuses policyholders is “deductible.” To demystify this important aspect of health insurance, this article will delve into the details of what a deductible is, how it works, and why it matters.
What Is a Deductible in Health Insurance?
Definition:
A deductible in health insurance refers to the specific amount of money you must pay out of your pocket for covered medical expenses before your insurance plan starts to contribute. It serves as a financial threshold that you need to meet before your insurer takes over the cost-sharing responsibilities.
How Does It Work?
1. Cost Sharing:
Health insurance is a partnership between you and your insurance company. The deductible is your portion of the cost-sharing agreement. Once you’ve paid this amount, the insurer typically starts sharing the expenses with you, either by covering a percentage of the costs or through copayments and coinsurance.
2. Types of Deductibles:
There are different types of deductibles in health insurance, including:
- Annual Deductible: This is the amount you need to pay each year before your insurance plan starts covering costs.
- Per-Incident Deductible: Some policies have a deductible applied to each medical incident or illness.
- Family Deductible: If you have a family plan, you may have a combined deductible for all family members or individual deductibles for each family member.
3. In-Network vs. Out-of-Network:
Deductibles can vary depending on whether you receive care from in-network or out-of-network healthcare providers. In-network services often have lower deductibles and cost-sharing, making them more affordable for policyholders.
Importance of Deductibles:

1. Cost Control:
Deductibles play a crucial role in controlling healthcare costs. When policyholders are responsible for a portion of the expenses, they have an incentive to make informed decisions about their medical care, which can help prevent unnecessary healthcare expenditures.
2. Premium vs. Deductible Trade-Off:
Choosing a health insurance plan involves a trade-off between premiums and deductibles. Plans with lower premiums often have higher deductibles, and vice versa. Understanding your healthcare needs and budget is essential when deciding which plan is right for you.
3. Financial Protection:
While deductibles require you to pay upfront, they provide financial protection against catastrophic medical expenses. Once you reach your deductible, your insurer typically covers a significant portion of the costs, reducing your financial burden.
Deductible Examples:
1. Scenario 1 – $1,000 Deductible:
- You have a health insurance plan with a $1,000 annual deductible.
- You undergo a covered medical procedure costing $3,000.
- You pay the first $1,000 (deductible), and your insurer covers the remaining $2,000.
2. Scenario 2 – $5,000 Deductible:
- You have a health insurance plan with a $5,000 annual deductible.
- You require surgery that costs $4,000.
- In this case, you would pay the full $4,000 because it doesn’t exceed your deductible amount.
Understanding what a deductible is and how it operates in health insurance is vital for making informed decisions about your coverage. It impacts your out-of-pocket costs, the affordability of your insurance plan, and the level of financial protection it offers. By considering your healthcare needs and budget, you can choose a health insurance plan that strikes the right balance between premiums and deductibles, ensuring that you have the coverage you need without breaking the bank.